Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is a crucial concept for businesses operating in India. It’s a mechanism where the tax liability is deducted by the employer from the employee’s income source before disbursing the in-hand salary. This deducted amount is then deposited to the government’s account. Understanding TDS rates with the latest changes is essential for accurate financial management.
In this article, we will explore the TDS rate charts for the financial year (FY) 2024-25 (Assessment Year 2025-26), we will also discuss the various income categories, applicable rates, and recent updates, helping you navigate the system effectively.
What is TDS?
Introduced in 1992 by the Income Tax Department of India, TDS or Tax Deducted at Source is a tax that aims to minimize tax avoidance. TDS applies to employee salaries, commissions, contractual payments, rent, professional fees, interests, and more.
The government under the Income Tax Act pre-decides the applicable TDS rates and deducts the amount in advance before giving it to the recipient. This way, the government collects taxes and tracks transactions efficiently.
Who Deducts TDS?
The responsibility of deducting TDS falls on the deductor, which can be:
- Individuals or HUFs (Hindu Undivided Families) making specified payments
- Companies
- Government agencies
- Local authorities
The deductor is obligated to deduct TDS only if the payment exceeds the prescribed threshold limit set by the Income Tax Act.
How is TDS Calculated?
TDS is calculated on the subtotal of the invoice without including GST, cess and other taxes.
Here are the steps to calculate TDS:
Step 1: Total Invoice Amount – (GST + cess + other taxes) = Invoice Subtotal
Step 2: Calculate the TDS and add it to the running balance of Auto TDS
Step 3: TDS gets added to the Auto TDS balance depending on the deduction date
What is a TDS Rate Chart?
A TDS rate chart is a reference table outlining the different types of income subject to TDS and the corresponding tax deduction rates. These rates are determined by the Income Tax Act of India and are periodically revised by the government. Referring to an accurate and updated TDS rate chart ensures you comply with tax regulations and avoid potential penalties.
Understanding TDS Rate Components
TDS rate charts typically categorize income sources and provide the corresponding TDS rate for each category. They may also differentiate rates based on factors like:
- Nature of Payment: The income being paid determines the applicable TDS rate. Common examples include salaries, interest income, professional fees, rent payments, etc
- PAN Status: Whether the recipient (deductee) provides a Permanent Account Number (PAN) significantly impacts the TDS rate. Not having a PAN typically attracts a higher deduction rate
- Tax Residency: The residency status of the recipient (resident or non-resident) plays a role in determining the TDS rate
The Importance of TDS Rate Charts
TDS rate charts serve as a reference point for both deductors and deductees. They specify the applicable tax rate to be deducted at source for various income streams. Knowing the correct TDS rate ensures:
Compliance: Following the prescribed TDS rates guarantees adherence to tax regulations, minimizing the risk of penalties and interest charges for non-compliance.
Accurate Tax Calculations: Both deductors and deductees can use the chart to estimate their tax liabilities, enabling them to plan their finances effectively.
Easier Tax Filing: By understanding the TDS already deducted, deductees can accurately calculate their final tax liability while filing their income tax returns.
Types of TDS
TDS is applicable across different verticals. These are the types of TDS:
Rent TDS: This type of TDS is deducted by individuals or businesses paying rent over and above a specified amount to their landlords.
Interest TDS: This TDS is deducted by banks on interest paid on fixed and recurring deposits and some other accounts with interests over a specified amount.
Salary TDS: The most common type of TDS, it is deducted by employers from the salary paid to their employees based on their respective income tax slab rates.
Commission TDS: This TDS is deducted by individuals or businesses who pay commissions to agents.
Professional Fee TDS: This TDS is deducted from fees paid to professionals like doctors, architects, lawyers, etc.
Dividend TDS: The TDS deducted by companies while paying for dividends made to shareholders on a specified amount.
TDS on Salaries
TDS on an employee’s salary is the reason behind the difference between in-hand salary and CTC. The employer deducts the tax from the employee’s salary and gives it to the government on the employee’s behalf.
TDS on salary comes under Section 192 of the Income Tax Act, 1961. Under this section, it becomes mandatory for the employer to calculate and deduct the income tax of every employee exceeding the basic exemption limit.
The TDS rate is not specified under Section 192; instead, it is deducted according to the income tax slab rates applicable to the taxpayer.
TDS on Interest Payments
Section 194A of the Income Tax Act deals with TDS on interest payments. However, it doesn’t include interest on fixed deposits, loans, and advances other than banks.
The amount shall be deducted by the payer in a financial year if it exceeds 40,000 INR where the payer is either a:
- Banking institution/bank or banking company
- Co-operative society engaged in the banking business
- Post office
There will be no TDS deduction on interest earned up to 50,000 INR by senior citizens. However, it is important to note that this interest should be earned from deposits in banks, post offices, and fixed and recurring deposit schemes.
It is to be noted that TDS on interest for non-resident Indians is under Section 195.
TDS on Rent
Rent is a payment made against the use of land, buildings, machinery, plants, furniture, or fittings for a defined period. TDS on rent is under Section 194-I of the Income Tax Act. This tax applies to those individuals who are generating income from rent by giving their property to be used.
TDS on Professional Fees or Technical Services
Businesses need services from professionals like architects, lawyers, chartered accountants, advertisers, etc. The tax deducted from the fee paid to these professionals is TDS on professional fees. Businesses also require technical services like taking technical or consultancy services which attracts TDS.
Covered under Section 194J, TDS on professional fees or technical services is deducted. Individuals and businesses making such payments are liable to deduct taxes at source.
TDS for Non-Resident Indians
The GOI collects TDS from non-residents under Section 195 of the Income Tax Law. This is applicable when a payment is made to an NRI or a foreign organization other than salary. NRIs are required to file their tax returns on the income earned in India.
TDS Rates in India
Different TDS rates in India apply to resident and non-resident payments and domestic and international companies functioning here. The individual or business is responsible for deducting TDS when paying income. Let us know the TDS rates across different categories.
TDS Rates Applicable for an Indian Resident (FY 2024-25)
Particulars |
TDS Rates |
Section 192: Salary payment
Section 192A: Premature withdrawal from EPF |
Normal Slab Rate
10%
|
Section 193: Interest on securities
a) any security of the Central or State Government; b) any debentures or securities for money issued by any local authority or a corporation established by a Central, State or Provincial Act; c) any debentures (listed on a recognised stock exchange) issued by a company where such debentures are ; d) interest on any other security |
10%
10% 10% 10% |
Section 194: Payment of any dividend |
10% |
Section 194A: Income in the form of interest (other than interest on securities). |
10% |
Section 194B: Income by way of lottery winnings, card games, crossword puzzles, and other games of any type |
30% |
Section 194BB: Income by way of horse race winnings |
30% |
Section 194C: Payment to contractor/sub-contractor.
a) Individuals/HUF b) Others |
1% 2% |
Section 194D: Insurance commission |
5% |
Section 194DA: Payment of any sum in respect of a life insurance policy.w.e.f. 1st September 2019, the insurer shall deduct tax (TDS) on the income portion comprised in the insurance pay-out. |
5%
|
Section 194EE: Payment of amount standing to the credit of a person under National Savings Scheme (NSS) |
10% |
Section 194F: Payment due to repurchase of a unit by Unit Trust of India (UTI) or a Mutual Fund |
20% |
Section 194G: Payments such as commission, etc., on the sale of lottery tickets |
5%
|
Section 194H: Commission or brokerage |
5% |
Section 194-I: Rent on a) Plant and Machinery
b) Land/building/furniture/fitting w.e.f 1st April 2019, tax deduction limit on rent is increased to Rs 2.4 lakhs p.a. from Rs 1.8 lakhs p.a. |
2% 10% |
Section 194-IA: Payment in consideration of transfer of certain immovable property other than agricultural land.
Section 194-IB: Rent payment by an individual or HUF not covered u/s. 194I Section 194-IC: Payment under Joint Development Agreements (JDA) to Individual/HUF |
1%
5% 10% |
Section 194J: Any sum paid by way of:
(a) Fee for professional services; (b) Remuneration/fee/commission to a director; (c) For not carrying out any activity in relation to any business; (d) For not sharing any know-how, patent, copyright etc. (e) Fee for technical services, and (f) Royalty towards the sale or distribution, or exhibition of cinematographic films. (g) Fees for technical services but payee is engaged in the business of operation of call centre |
10%
10% 10% 10% 2% 2% 2% |
Section 194K: Payment of any income for units of a mutual fund as per section 10(23D) or from the administrator or specified company |
10% |
Section 194LA: Payment in respect of compensation on acquisition of certain immovable property. |
10% |
Section 194LBA(1): Certain income distributed by a business trust to its unitholder |
10% |
Section 194LBB: Certain income paid in respect of units of an investment fund to a unitholder. |
10% |
Section 194LBC: Income frominvestment in securitisation fund
(a) Individual and HUF (b) Others |
25%
30% |
Section 194M: Certain payments by Individual/HUF (Limit- Rs 50 Lakhs) |
5% |
Section 194N: Cash withdrawal exceeding a certain amount (limit- Rs 1 crore).
In case Rs 20 lakh or more is withdrawn by the person not-filing ITR for the last three years, for which the due date of filing ITR has expired, the TDS rates shall be applicable as per below slabs- For the amount more than Rs.20 lakh but up to Rs. 1 crore, and And for the amount exceeding Rs. 1 crore |
2%
2% 5% |
Section 194O: For the sale of goods or provision of services by the e-commerce operator through its digital or electronic facility or platform. |
1% |
Section 194P: Tax deduction by specified banks while making payments (pension or interest) to specified senior citizens or age 75 years or more. |
Tax on total income as per rates in force |
Section 194Q: Payments to residents for the purchase of goods if the aggregate value of goods exceeds Rs 50 lakhs.(TDS is deductible on value exceeding Rs 50 lakhs) |
0.1% |
Any Other Income |
10% |
TDS Rate Chart for Non-Resident Indians for FY 2024-25
Particulars |
TDS Rate |
Section 192: Salary payment
Section 192A: Withdrawal from EPF before maturity |
Normal Slab Rate
10% |
Section 194B: Income from lottery winnings, card games, crossword puzzles, and other games |
30% |
Section 194BB: Income from horse race winnings |
30% |
Section 194E: Payment to non-resident sportsman (including an athlete) or an entertainer (not a citizen of India) or non-resident sports association. |
20% |
Section 194EE: Payment of amount standing to the credit of a person under National Savings Scheme (NSS) |
10% |
Section 194F: Payment due to repurchase of a unit by Unit Trust of India (UTI) or a Mutual Fund |
20% |
Section 194G: Payments such as commission, etc., on the sale of lottery tickets |
5% |
Section 194LB: Payment in respect of compensation on acquisition of certain immovable property. |
5% |
Section 194LBA(2): Payment like-
-interest income received or receivable to a business trust from SPV and distribution to its unitholders. -dividend income received from SPV by a business trust, in which it holds the entire share capital other than required to be held by the government or government body, and distribution to its unitholders. |
5%
10% |
Section 194LBA(3)- payment in the nature of income in the nature of rental income, out of real estate assets owned directly by such business trust, to unitholders. |
30% |
Section 194LBB: Payment of certain income by an investment fund to a unitholder. |
30% |
Section 194LBC: Income from investment in securitisation fund |
30% |
Section 194LC: Payment in the nature of interest for the loan borrowed in foreign currency by an Indian company or business trust against loan agreement or against the issue of long-term bonds*.
*If interest is payable against long term bonds listed in recognised stock exchange in IFSC |
5%
4% |
Section 194LD: Payment of interest on the bond (rupee-denominated) to Foreign Institutional Investors or a Qualified Foreign Investor. |
5% |
Section 195: Payment of any other sum to NRI:Income on investments made by NRI citizen;
Income by way of LTCG referred to in section 115E in the case of NRI; Income by way of LTCG under section 112(1)(c)(iii); Income by way of LTCG under section 112A; Income by way of STCG under section 111A; Any other income by way of LTCG; Interest payable on money borrowed by the government or Indian concern in foreign currency; Income from royalty payable to the Indian concern, by government or Indian concern, for the copyright in a subject referred in the first proviso of section 115A or computer software referred to in the second proviso of section 115A Income from royalty payable to the Indian concern by government or Indian concern in pursuance of an agreement on matters related to industrial policy; Income from technical fees to the Indian concern by government or Indian concern in pursuance of an agreement on matters related to industrial policy; Any other income. |
20%
10% 10% 10% 15% 20% 20% 10% 10% 10% 30% |
Section 196B: Income (including LTCG) from units of an offshore fund. |
10% |
Section 196C: Income (including LTCG) from foreign currency bonds or GDR of an Indian company |
10% |
Section 196D: Income (excluding dividend and capital gain) from Foreign Institutional Investors. |
20% |
TDS Rate Chart for Domestic Company for FY 2024-25
Particulars |
TDS Rate |
Section 192: Salary payment
Section 192A: Withdrawal from EPF before maturity |
Normal Slab Rate
10% |
Section 193: Interest on securities:
a) any security of the Central or State Government; b) any debentures or securities for money issued by any local authority or a corporation established by a Central, State or Provincial Act; c) any debentures (listed on a recognised stock exchange) issued by a company where such debentures are; d) interest on any other security |
10%
10% 10% 10% |
Section 194: Dividend payment |
10% |
Section 194A: Interest payment (other than interest on securities) |
10% |
Section 194B: Income from lottery winnings, card games, crossword puzzles, and other games |
30% |
Section 194BB: Income from horse race winnings |
30% |
Section 194C: Payment to contractor/sub-contractor:
a) Individuals/HUF b) Others |
1%
2% |
Section 194D: Commission from insurance |
10% |
Section 194DA: Life insurance policy payment w.e.f. 1st September 2019, the insurer shall deduct tax (TDS) on the income portion comprised in the insurance pay-out |
5% |
Section 194EE: Payment standing to the credit of a person under National Savings Scheme (NSS) |
10% |
Section 194F: Payment from repurchase of a unit by Unit Trust of India (UTI) or a Mutual Fund |
20% |
Section 194G: Commission on the sale of lottery tickets |
5% |
Section 194H: Commission or brokerage |
5% |
Section 194-I: Rent on a) Plant and Machinery
b) Land/building/furniture/fitting w.e.f 1st April 2019, tax deduction limit on rent is increased to Rs 2.4 lakhs p.a. from Rs 1.8 lakhs p.a. |
2%
10% |
Section 194-IA: Payment from transfer of certain immovable property other than agricultural land
Section 194-IC: Payment under Joint Development Agreements (JDA) to Individual/HUF |
1%
10% |
Section 194J: Any sum paid by way of:
(a) Fee for professional services; (b) Remuneration/fee/commission to a director; (c) For not carrying out any activity in relation to any business; (d) For not sharing any know-how, patent, copyright etc. (e) Fee for technical services, and (f) Royalty towards the sale or distribution, or exhibition of cinematographic films. (g) Fees for technical services but payee is engaged in the business of operation of call centre |
10%
10% 10% 10% 2% 2% 2% |
Section 194K: Payment from income for units of a mutual fund as per section 10(23D) or from the administrator or specified company |
10% |
Section 194LA: Payment from respect of compensation on acquisition of certain immovable property |
10% |
Section 194LBA(1): Certain income distributed by a business trust to its unitholder |
10% |
Section 194LBB: Certain income paid in respect of units of an investment fund to a unitholder |
10% |
Section 194LBC: Income from investment in securitisation fund |
10% |
Section 194M: Certain payments by Individual/HUF (Limit- Rs 50 Lakhs) |
5% |
Section 194N: Cash withdrawal exceeding a certain amount (limit- Rs 1 crore)
In case Rs 20 lakh or more is withdrawn by the person not-filing ITR for the last three years, for which the due date of filing ITR has expired, the TDS rates shall be applicable as per below slabs- For the amount more than Rs.20 lakh but up to Rs. 1 crore, and And for the amount exceeding Rs. 1 crore |
2%
2% 5% |
Section 194O: For the sale of goods or provision of services by the e-commerce operator through its digital or electronic facility or platform. |
1% |
Section 194Q: Payments to residents for the purchase of goods if the aggregate value of goods exceeds Rs 50 lakhs.(TDS is deductible on value exceeding Rs 50 lakhs) |
0.10% |
Any Other Income |
10% |
TDS Rate Chart for Foreign Companies for FY 2024-25
Particulars |
TDS Rate % |
Section 194B: Income from lottery, card games, crossword puzzles, and other games |
30% |
Section 194BB: Income from horse race winnings |
30% |
Section 194E: Payment to NRI sportsman or an NRI entertainer or NRI sports association |
20% |
Section 194G: Commission on the sale of lottery tickets |
5% |
Section 194LB: Compensation on acquisition of some immovable property |
5% |
Section 194LBA(2): Payment such as –
– interest received or receivable to a business trust from SPV and distribution to its unitholders – dividend received from SPV by a business trust where it holds the entire share capital apart from required to be held by the government or government body, and distribution to its unitholders |
5%
10% |
Section 194LBA(3): Rental income from real estate assets owned directly by such business trust to unitholders |
40% |
Section 194LBB: Payment of income by an investment fund to a unitholder |
40% |
Section 194LBC: Securitisation fund investment income |
40% |
Section 194LC: Payment from the interest of the loan borrowed in foreign currency by an Indian company or business trust against loan agreement or against the issue of long-term bonds*.
*If interest is payable against long term bonds listed in recognised stock exchange in IFSC |
5%
4% |
Section 194LD: Interest payment on the bond (rupee-denominated) to Foreign Institutional Investors or a Qualified Foreign Investor |
5% |
Section 195: Payment of any other sum, such as-Income by way of LTCG under section 112(1)(c)(iii);
Income by way of LTCG under section 112A; Income by way of STCG under section 111A; Any other income by way of LTCG; Interest payable on money borrowed by the government or Indian concern in foreign currency; Income from royalty payable to the Indian concern, by government or Indian concern, for the copyright in a subject referred in the first proviso of section 115A or computer software referred to in the second proviso of section 115A (an agreement made after 1st March 1976); Income from royalty payable to the Indian concern by government or Indian concern in pursuance of an agreement on matters related to industrial policy. Where the agreement is made after- 31st March 1961 but before 1st April 1976-31st March 1976 Income from technical fees to the Indian concern by government or Indian concern in pursuance of an agreement on matters related to industrial policy. Where agreement is made after- 29th February 1964 but before 1st April 197631st March 1976 Any other income. |
10%
10% 15% 20% 20% 10% 50% 10% 50% 10% 40% |
Section 196B: Income from units of an offshore fund (including LTCG) |
10% |
Section 196C: Income from foreign currency bonds or GDR of an Indian company (including LTCG) |
10% |
Section 196D: Income from foreign institutional investors (excluding dividend and capital gain). |
20% |
New TDS Provisions
Under the Union Budget 2023, there were certain changes in tax provisions according to which TDS was introduced on certain categories like online gaming, and mutual funds while there were relaxation for some categories. Let us explore the changes.
Introduction of TDS on Online Gaming (Section 194BA)
According to the new provision, for all those who make money via online gaming platforms, there will be a 30% deduction on TDS on the net winning amount. Tax will be deducted when the winning amount will be withdrawn from the account. If the winning amount is not withdrawn during the financial year, then tax will be deducted on the winning amount in the account.
TDS on NRI Income from Mutual Funds (Section 196A)
NRIs who are earning income from investment in mutual funds in India can produce a Tax Residency Certificate. This will help them get TDS benefit according to the tax treaty.
Reduction in TDS on PF Withdrawal Without PAN (Section 192A)
The GOI has reduced the TDS rate to 20% on PF withdrawals for employees without a PAN card.
TDS on Interest Earned from Securities (Section 193)
Tax will be deducted on interest on specified securities. There will be no exemption from TDS on interest from debentures listed.
TDS on Co-operative Society Cash Withdrawal (Section 194N)
Tax will be deducted on the withdrawal of cash by cooperative societies if the amount is more than Rs 3 crore and not Rs 1 crore which was the previous limit.
How to file TDS
It is important to know that before filing TDS, registration on the income tax portal is mandatory.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to register on the income tax portal
Step 1: Visit the income tax website and register
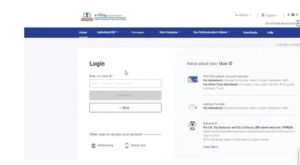
Step 2: Select the Category as Tax Deductor and Collector
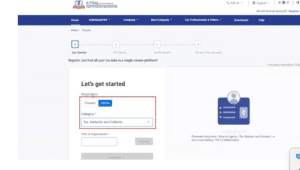
Step 3: Enter your organization’s and validate it.
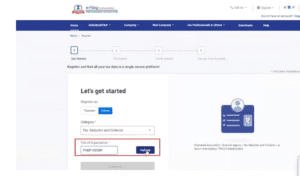
Step 4: If TAN is registered with TRACES and available in the database; but the registration is pending for approval, view the details and continue.
If TAN is not registered with TRACES and registration request is pending for approval, register with TRACES and then you will be redirected to e-filing registration page.
If TAN is already registered and request is pending for approval; an error message will be displayed to withdraw the registration process.
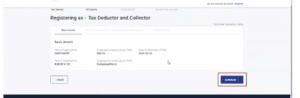
Step 5: Provide the details as required and continue.
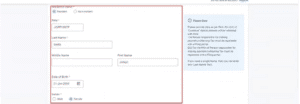
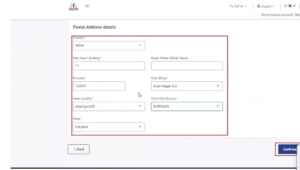
Step 6: Enter the contact details and postal address as required.
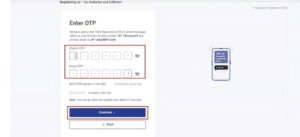
Step 7: Enter the OTPs sent to registered email Id and phone number.
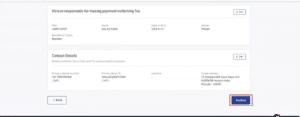
Step 8: Review the details provided and confirm.
Step 9: Enter your password as desired and click on Register.
A message for successful registration will appear on the screen along with the transaction ID.
After successful registration, file the TDS:
- Visit https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal/ and download the challan
- Log in to your account
- Click on e-File – E-Pay Tax – Payment History
- Click on the challan you want and download the same
To know more about TDS, follow the frequently asked questions below.
FAQs
Is TDS mandatory for companies?
Businesses must deduct TDS while giving salaries and taking professional and technical services.
What is the TDS rate on salary?
The TDS rate on salary depends on the tax slab of the individual. TDS deduction on salary ranges from 5% to 30% for all employees who come in an annual salary of 3 lakhs and above.
What is the rate of TDS on commission?
The rate of TDS on commission paid to agents or brokers is 5% under Section 194H of the Income Tax Act.














