Introduction
A financial system is the backbone of any economy, linking various types of institutions, markets, and participants such as governments, corporations, and individuals. By channelling capital from surplus holders to borrowers and deficit units, the financial system makes sure resources are efficiently allocated, economic stability is maintained, and growth can continue. In addition to streamlining capital movements, the financial system is also essential in managing risk, delivering liquidity, and ensuring optimal resource allocation.
It supports innovation and trade – without it, the economy could not continue evolving. This blog examines the components, functions, and importance of a financial system.
Definition:
Financial System refers to the network of financial institutions, markets, instruments, and services that facilitate the flow of funds between savers and borrowers
What is a Financial System?
A financial system is the network that helps money flow smoothly in an economy. It connects people or businesses who have extra money (savers or investors) with those who need money (borrowers or companies) to grow or invest.
In simple words, the financial system makes sure money moves from where it’s saved to where it’s needed, helping businesses expand, creating jobs, and keeping the economy active.
According to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the financial system includes all institutions, markets, and rules that help in saving, lending, and investing money safely. It acts as the backbone of an economy, influencing how people save, spend, and invest.
Also Read: What is Corporate Accounting?
A healthy financial system requires rules for conducting financial business and for who can participate in it. Those rules have to be open and transparent, regulated by the government to ensure that borrowers pay back what they owe, and lenders can rely on their loans. The financial system in India is composed of a complex array of institutions, including public and private sector banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and microfinance institutions, which all contribute to the financial needs of the economy.
Also Read: What is Financial Structure
Features :
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Transfers funds from savers to investors to promote economic growth.
- Liquidity Creation: Ensures businesses and individuals can easily convert assets into cash.
- Financial Stability: Reduces economic volatility through strong regulation and transparent operations.
- Capital Formation: Encourages savings and investments that build a nation’s wealth.
Components of a Financial System
The financial system has many essential pieces, and they each contribute to the proper functioning of the capital flows.
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are the bridge between savers and borrowers. These include commercial banks, insurance firms, pension funds, and investment companies. Their primary purpose is to collect deposits from savers and offer loans to individuals and companies, which allows for the healthy circulation of capital in the economy.
Public sector banks such as the State Bank of India are vital for financing India’s rural and urban sectors. Private banks such as HDFC and ICICI Bank target high-income earners and offer consumers sophisticated financial products. Regional rural banks cater to agricultural and small-scale industries. Non-bank financial institutions such as microfinance companies and insurance corporations offer specific financial products to customers and businesses are platforms where financial that mobilize savings and manage risk.
Financial Markets
Financial markets are the places where financial instruments such as shares, bonds, and derivatives are traded. These markets provide liquidity and enable both individuals and enterprises to buy and sell securities quickly and efficiently. Financial markets are also a source of long-term capital, which allows enterprises to fund their business, invest in new ventures, and grow.
India’s financial markets, dominated by the Stock Exchanges including Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE), are essential for raising capital for public and private sector enterprises. The bond market in India enables the government and companies to generate long-term funds using debt.
Financial Instruments
The securities that are traded in the markets are referred to as financial instruments. Popular examples of these instruments include equities or shares, bonds, commodities, derivatives such as options and futures, etc. These securities represent either ownership in a company (equities) or debt (bonds) and may offer an investor a chance to make a return.
Also Read: What is the Cost of Debt?
Financial instruments are critical to the functioning of the financial system. They enable the transfer of financial risk, the raising of capital, and the allocation of resources. With equities and bonds, companies and governments can sell shares of their ownership and debt securities to raise capital. Derivatives such as options and futures provide ways of hedging risk associated with fluctuations in the price of underlying assets.
Financial Services
Financial services refer to a collection of activities that enable consumers and companies to manage their financial resources.
These services include banking, insurance, investment management, and wealth advisory. A bank provides fundamental services to consumers and companies, such as savings accounts, loans, and credit. Insurance companies provide products that protect individuals and companies against financial losses resulting from events outside normal circumstances.
In India, there has been a boom in financial services over the past few years, thanks to growing digital banking, fintech, and trading infrastructure, in addition to financial inclusion programmes that have pushed financial services into the rural, unbanked parts of the country.
Currency
Currency is the medium of exchange. It helps facilitate trade and allows consumers and businesses to conduct transactions. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) controls the economy’s supply of money, keeping inflation in check and the currency stable. India’s currency system is crucial for both domestic and global trade to operate in a secure way, where both corporations and individuals can conduct their business successfully.
How does the Financial System Work in India?
The financial system acts as a bridge between savers and borrowers, helping money move smoothly through the economy. It ensures that savings are converted into productive investments — supporting business growth, job creation, and overall economic development.
In simple terms, the financial system allows people and organizations who have extra money to lend or invest it, while those who need funds can borrow it efficiently. This process maintains the balance of liquidity, stability, and financial growth in the economy.
Step-by-Step Working of the Financial System:
- Savings Generation:
Individuals, households, and businesses deposit their extra money into banks or invest in instruments like mutual funds or bonds. - Financial Intermediation:
Financial institutions such as banks, NBFCs, and mutual funds collect these savings and act as intermediaries between savers and borrowers. - Investment and Lending:
The collected funds are then lent to companies, industries, and governments for business expansion, infrastructure, and development projects. - Returns and Reinvestment:
Borrowers repay the loans with interest or profits, which are returned to investors as dividends, interest, or capital gains — completing the money cycle. - Regulation and Stability:
Regulatory bodies like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), SEBI, and IRDAI ensure transparency, protect investors, and maintain financial stability.
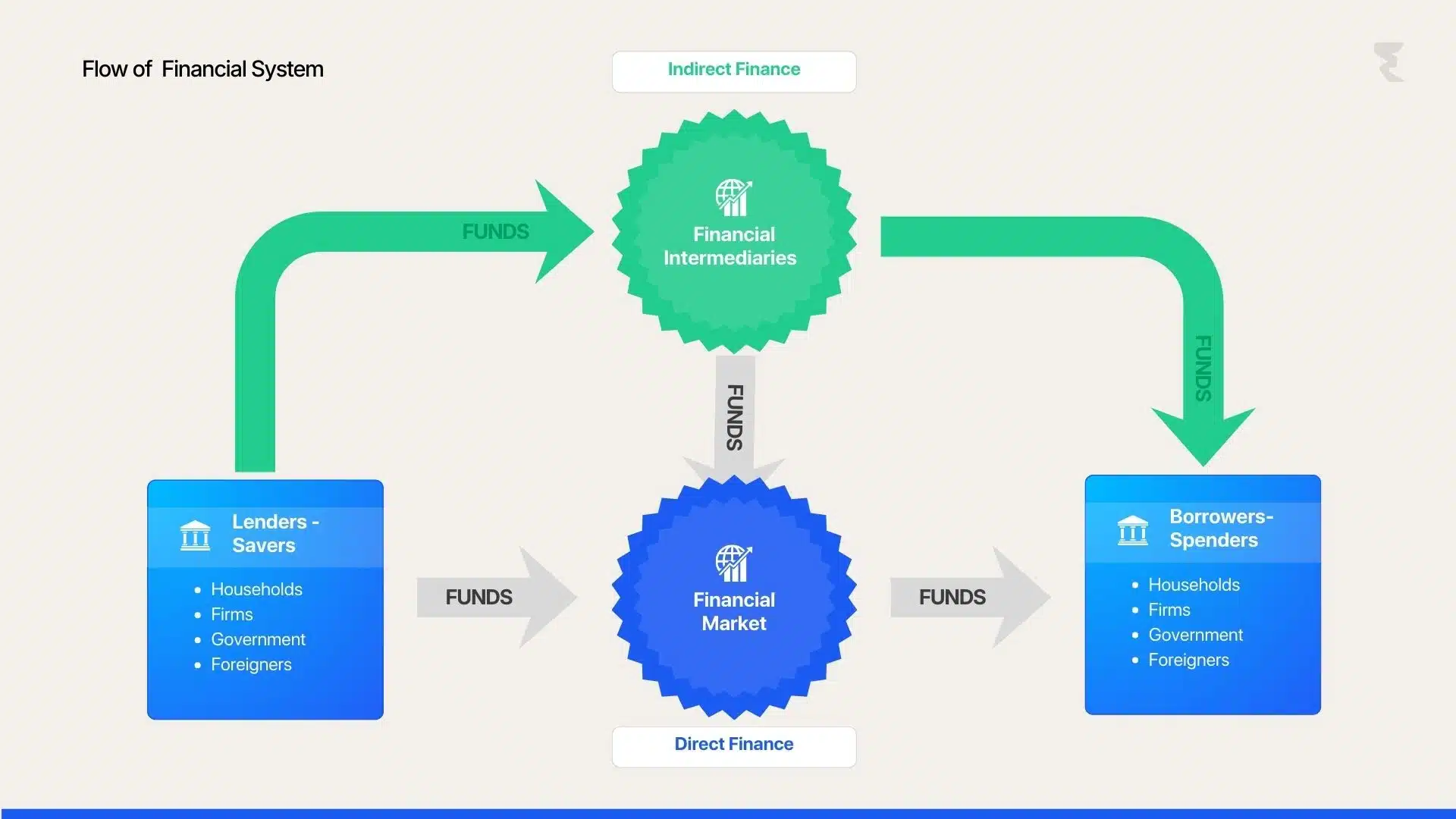
Flow of Funds in a Financial System
Participants |
Function |
Example |
|---|---|---|
Savers (Households, Investors) |
Provide surplus funds to the system |
Deposits, Investments |
Financial Institutions |
Intermediaries that channel funds |
Banks, NBFCs, Mutual Funds |
Borrowers (Businesses, Government) |
Use funds for growth and development |
Business loans, Bonds |
Regulatory Bodies |
Supervise and maintain trust |
RBI, SEBI, IRDAI |
Flow of Financial System:
What is a Financial Market?
In simple terms, the financial market connects people who have extra funds (investors or savers) with those who need funds (businesses or governments). This exchange supports capital formation, encourages investment opportunities, and contributes to economic growth.
Difference Between Financial System and Financial Market:
Aspect |
Financial System |
Financial Market |
|---|---|---|
Definition |
A network of financial institutions, instruments, and markets that facilitates fund flow. |
A part of the financial system where financial instruments are traded. |
Scope |
Broader — includes banks, financial institutions, and regulatory bodies. |
Narrower — focuses mainly on trading and investment activities. |
Function |
Ensures overall financial stability and money circulation. |
Provides liquidity, price discovery, and investment avenues. |
Classification of Financial Markets
The financial market is broadly divided into four major types, each serving a unique function:
- Money Market:
Deals with short-term financial instruments (less than one year) such as Treasury Bills, Certificates of Deposit, and Commercial Papers.
Example: RBI manages liquidity through money market operations. - Capital Market:
Involves long-term investments like shares, debentures, and bonds. It helps companies raise funds for business expansion.
Example: Stock exchanges like BSE and NSE facilitate equity trading in India. - Derivatives Market:
Allows trading of financial contracts based on underlying assets such as stocks, commodities, or indices. It helps in risk management and speculation. - Foreign Exchange Market (Forex):
Involves the trading of currencies and determines exchange rates. It plays a key role in global trade and investment.
Components of the Financial Market
The financial market operates through two main segments that ensure liquidity and capital growth:
- Primary Market:
This is where new securities (like IPOs) are issued for the first time. It helps companies raise fresh capital directly from investors. - Secondary Market:
It deals with the trading of existing securities, providing investors with liquidity and flexibility.
Example: BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) and NSE (National Stock Exchange) are India’s largest secondary markets.
Functions of a Financial System
The functions of a financial system play a key role in the smooth functioning of the economy. Let’s explore some of the core functions.
Also Read: What is Financial Statement Analysis
Capital Allocation
It works efficiently, allocating capital, moving money from those who have savings to spare to those who need borrowing. Financial intermediaries such as banks, stock exchanges, and investment funds accelerate the process by assessing the creditworthiness of the debtor and ensuring that capital flows to the most productive uses. This process serves as a key accelerator of economic development by funding investment in infrastructure, education, and technology, among other areas.
In India, the financial system has been integral to funding huge infrastructure projects ranging from roads to airports to power stations, which help create long-term growth.
Risk Management
Risk management is another important task. Many financial instruments, such as insurance, derivatives, and diversified investment portfolios, allow individuals and businesses to reduce risk. For instance, some insurance policies protect against accidents, storms, and business losses; some derivatives enable hedging against movements in commodity prices or financial asset prices.
Financial institutions are also important in assessing the credit risk of those wishing to borrow and ensuring the availability of credit only to those who are capable of repayment.
Liquidity Provision
A healthy financial system provides liquidity. In this context, the term liquidity is used to describe the availability of cash or assets, which are freely convertible into cash, that can be used to cover short-term liabilities. For example, money markets and commercial banks make short-term loans available, helping to ensure that businesses can continue operating smoothly as they meet their financial obligations.
Liquidity management in India has been an important priority for the RBI during periods of stress in the financial markets, such as during the global financial crisis, or more recently, the COVID-19 pandemic.
Payment Mechanism
The financial system facilitates payment for transactions between businesses, corporations, governments, and individuals. Payment systems include traditional banking services such as wire transfers and cheques, as well as the new digital payment mechanisms. The volume of digital payments has been growing in India thanks to the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and mobile banking platforms, which are transforming the payment experience in India. Now, payments are faster, safer, and available to everyone.
What Factors Affect the Stability of a Financial System?
The stability of a financial system depends on how efficiently money, credit, and investments flow across the economy. A stable system ensures that banks, markets, and financial institutions can operate smoothly even during economic ups and downs.
Below are the major factors that influence financial system stability:
1. Economic Growth and Inflation
- Strong and consistent economic growth strengthens the financial system by increasing investment and employment.
- However, high inflation reduces purchasing power and weakens investor confidence, making the system more volatile.
- Balanced growth and stable prices are crucial for long-term stability.
2. Monetary and Fiscal Policies
- Monetary policy (managed by the RBI) controls interest rates and liquidity in the economy.
- Fiscal policy (managed by the government) influences taxation and spending patterns.
Together, these policies help maintain economic stability, control inflation, and ensure smooth credit flow.
3. Interest Rates and Liquidity
- Interest rate fluctuations directly affect borrowing, lending, and investment decisions.
- Adequate liquidity in banks and financial institutions ensures that credit is available when needed.
- Sudden liquidity shortages or high rates can cause instability in financial markets.
4. Technological Advancements
- Innovations like FinTech, AI-driven banking, and digital payments have made financial services faster and more inclusive.
- However, increased digitization also raises cybersecurity and fraud risks, which can impact system stability if not managed properly.
5. Global Economic Trends
- Global events such as oil price fluctuations, trade wars, or geopolitical tensions can affect domestic markets.
- Integration with global markets means that financial shocks in one country can quickly spread to others.
- Maintaining diversified financial portfolios and strong regulatory oversight helps reduce such risks.
Conclusion
The financial system underpins the economy by enabling efficient investment, risk management, and liquidity. By linking savers, investors, and borrowers, it fosters the growth of businesses, job creation, technological advancement, and economic growth. In India, the financial system has played a crucial role in infrastructure construction, business development, and encouraging global trade.
With more complicated economies, the function of a financial system to maintain stability and enable inclusive growth becomes increasingly important. Continuous reforms, innovations, financial literacy, and technological upgrades are key to resilience. A properly governed, transparent financial system will benefit businesses, governments, and the wider society at large, paving the way for sustained economic growth.
FAQs
1. What is the role of financial markets in determining interest rates?
Financial markets help determine interest rates by reflecting the supply and demand for capital. When there is a higher demand for capital, interest rates rise, while an excess supply of capital tends to lower rates. This dynamic impacts borrowing costs for businesses and individuals.
2. How does the financial system influence economic growth?
The financial system promotes economic growth by providing businesses with access to capital, facilitating trade, supporting entrepreneurship, and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
3. What role does the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) play in the financial system?
The RBI regulates India’s financial system by controlling money supply, setting interest rates, and overseeing financial institutions to ensure stability and liquidity.
4. How do financial systems manage risks?
Financial systems manage risks through diversification, insurance, derivatives, and regulatory frameworks that ensure financial institutions operate safely and prudently.
5. Why is liquidity important in a financial system?
Liquidity ensures that financial institutions can meet their short-term obligations and that capital is available when needed, reducing the risk of systemic financial failures.
6. How do financial markets differ from financial institutions?
Financial markets facilitate the trading of assets like stocks and bonds, while financial institutions, such as banks and insurance companies, act as intermediaries between savers and borrowers.
7. What are non-banking financial institutions (NBFIs)?
NBFIs include entities like insurance companies, pension funds, and investment firms that provide financial services but do not hold banking licenses.
8. How does the financial system promote entrepreneurship?
The financial system provides entrepreneurs with access to capital through loans, venture capital, and equity markets, helping them fund and grow their businesses.
9. What are financial instruments, and why are they important?
Financial instruments are assets like stocks, bonds, and derivatives, which allow for the transfer of capital in financial markets, providing liquidity and investment opportunities.
10. How does technology impact the financial system?
Technologies like fintech, blockchain, and digital payments enhance efficiency, accessibility, and security in the financial system, making financial services available to a broader audience.
11. Why is the Financial System Important for Economic Growth?
The financial system is vital for economic growth because it acts as the bridge between savings and investments. It channels funds from individuals and institutions who have excess money (savers) to those who need it for productive purposes (businesses, industries, and governments). This circulation of money fuels business expansion, job creation, and overall development.
12. What is the Indian Financial System?
The Indian Financial System refers to the network of institutions, markets, instruments, and services that help in the flow of funds within the Indian economy. It connects savers, investors, businesses, and the government, ensuring the smooth circulation of money for growth and development.
In simple terms, it is the backbone of India’s economy, helping people save, invest, borrow, and manage money safely through regulated financial channels.