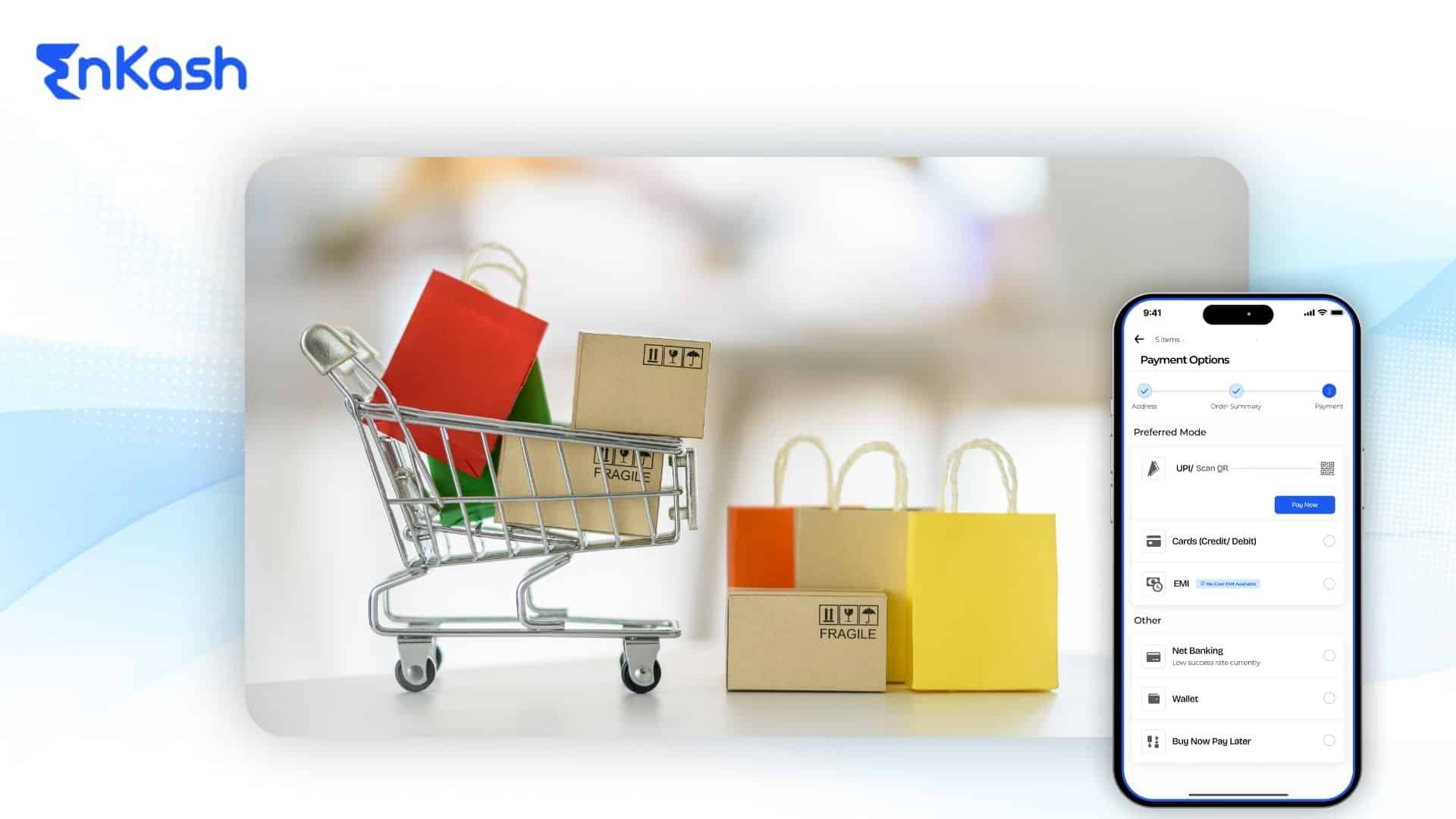
E-commerce has changed how businesses sell and how customers shop. A key part of this change is the E-commerce payment system. These are the tools and methods that make online payments possible. In simple terms, E-commerce payment systems (also called electronic payment systems in E-commerce) help businesses accept payments online in return for their products or services.
Why are online payment systems so important? The reason is that these systems bring more convenience, global access, and faster money exchange. Today, customers expect a checkout that is simple and secure.
If a site’s payment process is slow or lacks their preferred method or looks fishy, buyers may leave without paying. This is not just a psychological assumption. Studies have shown that cart abandonment rates spike when the checkout process is slow, confusing, or lacks preferred payment methods. That’s why offering quick payment solutions and a secure process is vital. It helps build trust and increase sales.
What is an E-commerce Payment System?
An E-commerce payment system is a digital setup that handles online money transactions. It includes the software and services that let customers pay online and allow merchants to receive payments directly into their bank accounts.
Unlike cash transactions, this system works over the internet. It uses card networks, online banking, or mobile wallets instead of physical money or cheques.
An E-commerce payment system involves many parties. This includes the customer, the online seller, banks, and payment service providers like payment gateways or processors. When a customer pays online, the system securely sends the payment data through a gateway. In simple terms, the payment system connects the online store to the banks. It moves the money from the buyer to the seller.
There are many banks that offer digital services today. These include facilities like fund transfers, online banking, and bill payments. These are part of digital banking services that support the E-commerce ecosystem. These services make banking easier and more accessible. E-commerce has pushed banks to improve. It has made digital transactions smoother and faster.
Read more: How Businesses Can Accept Payments Online: Top Payment Gateway Providers & Platforms in India
Types of Electronic Payment Systems in E-Commerce
Let’s check out below the most common types of electronic payment systems used in e-com transactions:
Credit Cards
Credit cards are a basic part of how people pay online today. They let someone buy a product now and pay the bank later. Most online shops accept credit cards. Big companies like Visa, Mastercard, and American Express handle these payments. They are trusted because they offer buyer safety and help with refund issues.
You may feel credit cards are too useful, but there are a few downsides as well. Businesses have to pay a fee every time someone uses a credit card. Yes, that’s the truth. There’s also the risk of fraud. If a card gets stolen, the business might lose money due to chargebacks. Still, credit cards are widely used.
Debit Cards
Debit cards look like credit cards, but they work differently. When you use a debit card, money comes straight out of your bank account. You can only spend what’s already there. To use one, you need an account with enough balance. Many people like this because it helps them stay within budget.
Debit cards use the same networks as credit cards, like Visa, Mastercard, or RuPay. They also follow the same security rules. You may be asked for a PIN or a one-time password to confirm the payment. For businesses, debit cards usually cost less to process than credit cards. In India, due to regulatory caps by the RBI, debit card transaction fees are often similar to or lower than those for credit cards
However, debit cards don’t offer rewards or credit. They also limit you to the amount in your account. Still, they are very common in online shopping. In India, many people use debit cards because they like to pay without taking on debt.
Digital Wallets (E-Wallets)
A digital wallet is an app or online tool that saves your card or bank details. These wallets let you pay with a few taps. You can use saved card details or money already in the wallet. Many people now prefer this method.
People like wallets because they are quick and easy. You don’t have to enter card numbers every time. They also make payments safer. Your card number is hidden, and you may need to use a fingerprint or password to approve the payment.
Shops also benefit. How? If they support wallets that people trust, more customers will finish their orders. But not every shop supports every wallet. That can be a problem. Also, wallets can still face hacking risks. If one gets hacked, people might lose trust.
Even with those risks, wallets have become a big part of online shopping. They work especially well on mobile phones.
Bank Transfers and Net Banking
Bank transfers let you pay straight from your bank account. You don’t need a card. A common way to do this is through net banking. At checkout, you pick your bank from a list. Then, you log in to your bank’s site and approve the payment. It’s a direct transfer from your account to the seller’s account.
Many people feel safe using this method. You never share your card details. Also, your bank may ask for a password or an OTP to confirm the payment. This adds an extra layer of safety.
Other ways to send money directly from your bank include EFT or ACH transfers. But there are downsides, too. Some transfers are slow. It might take a full day or more for the payment to go through. That’s not ideal when customers want quick results. Also, switching to the bank’s website can interrupt the flow of checkout.
Even with those issues, bank transfers are still useful. They work well for people who don’t have cards. They are also used in business-to-business sales or for big orders, where buyers prefer direct bank payments.
Mobile Payments (Includes UPI and QR-Based Payments)
As mobile phones have become common, mobile-based payments have grown rapidly and turned into a widely used way for payments. Mobile payments include any payment made using a smartphone or mobile device. This includes digital wallets, since many wallets are apps, and other payment methods.
NFC Contactless Payments:
Various platforms let users tap their phone or pay online using saved card details. They work through near-field communication. In E-commerce apps, this type of payments act as one-tap payment options.
QR Code Payments and UPI:
In countries like India, QR-code and mobile number-based payments have become very popular. UPI (Unified Payments Interface) is a real-time system that lets users pay directly from their bank accounts. They can pay by entering a virtual address or scanning a QR code. UPI is now India’s top e-payment method (As of 2024, UPI accounts for over 70% of India’s digital payment volumes, according to NPCI data). It allows instant bank transfers through E-commerce payment system apps.
SMS and Carrier Billing:
Some payments can be made by sending a text message. Others are added to the mobile phone bill. This is mostly used for micro-payments such as mobile gaming credits or digital donations.
Mobile payments are very convenient. A customer can tap or scan without typing details. Security is higher due to device checks like biometrics, built-in encryption, and token systems.
But there are a few problems. Not all stores support every mobile method. Also, customers need a phone that works with these apps and must know how to use them. Still, UPI proves mobile payments can replace cash if set up well.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL)
Buy Now, Pay Later is a new way to pay. It has quickly become popular, especially with younger shoppers. BNPL services let buyers split payments over time. BNPL services often offer interest-free installments if paid on time, though some may charge processing or late fees depending on the provider. At checkout, the BNPL company approves the customer, sometimes using a soft credit check. Then it pays the full amount to the seller right away. The customer pays back in parts over weeks or months. This lets buyers shop now and pay later. It can increase spending and sales.
BNPL is growing fast. Shoppers like the flexible payment and smooth checkout experience. But there are risks as well. BNPL can lead to overspending. Some users may miss payments and fall into debt.
BNPL can indeed attract more buyers, especially for high-value items. But they should choose a reliable BNPL provider to avoid problems.
Prepaid Cards (Gift Cards)
Prepaid cards are loaded with a fixed amount of money. They can be physical or digital. Examples are gift cards for online stores or prepaid Visa or Mastercard cards. Customers can shop online with these cards until the balance runs out. Prepaid cards help control spending. You can’t spend more than what’s on the card. They’re good for people without a regular card or who don’t want to link a bank account.
Many prepaid cards are backed by Visa or Mastercard. This means they work wherever those cards are accepted. No bank account or credit check is needed to get one. You can even buy them with cash. Prepaid cards allow users to shop online without sharing bank details. In India, KYC-compliant prepaid cards are required for larger transactions, as per RBI norms. They offer control and safety. If lost or hacked, only the card’s balance is at risk. Unlike cash, they can be replaced if lost.
But there are downsides. Some cards charge fees to activate or maintain. If the purchase is more than the card’s balance, the payment may fail or need to be split. They’re useful for selling gift cards or for users who prefer cash-loaded cards.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency payments use digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or stablecoins. These currencies are based on blockchain and are not controlled by any government. This independence is part of their appeal. In the E-commerce payment system, when someone pays with crypto, the seller gets coins or tokens instead of regular money. Unless the seller uses a service to instantly convert it, they keep the crypto. Crypto payments offer global access. Anyone with the internet can send money across borders quickly, without banks.
In some cases, fees are lower because there are fewer middlemen. Crypto is also secure. It uses cryptography, and users control their funds. Since cryptocurrencies work outside the banking system, individual transactions cannot be blocked – though governments may regulate access to exchanges. Crypto has its challenges; prices change fast, which makes it hard to set stable prices. Not many online sellers accept crypto yet. Also, using crypto takes some tech skills. Users need to set up a wallet, handle private keys, and know how to manage it safely. Unlike cards, crypto payments cannot be reversed if something goes wrong. That makes refunds tricky.
Cash on Delivery (COD)
Cash on Delivery is a payment method where customers pay in person after ordering online. The buyer places the order and pays with cash or card when the product arrives. This method is common in places where trust in online payments is low or where many people don’t have digital payment options.
Customers like COD because it feels safe and simple. They pay only after checking the product. It needs no online setup, no card, no account. So it’s accessible for those without banking.
In India, many people first tried online shopping through COD, as they were unsure about fraud or product quality. But COD also brings issues. Customers must have cash ready and be present at delivery, which can be inconvenient. For sellers also, COD creates problems.
There are more returns, some buyers refuse delivery, and the time to get the money is longer. Courier companies also charge extra for handling cash. Worldwide, COD is fading as digital payments grow. However, it still matters for some users, but businesses must weigh the costs and benefits before offering it.
Security and Fraud Prevention in E-Commerce Transactions
Here are some key security considerations and measures in E-commerce payment systems.
Encryption of Data
All payment data shared online must be encrypted. This usually means using SSL/TLS (HTTPS) on your site so credit card details, passwords, and personal data can’t be read if intercepted.
When a customer types their card details on a secure checkout page, the data is encoded. You can usually spot this by the padlock icon in the browser. The payment gateway keeps the data encrypted when sending it to the bank. Encryption scrambles the data. Only those with the right keys can read it.
PCI DSS Compliance
If your business deals with card data in any way, by storing, processing, or transmitting it, you must follow PCI DSS rules. They cover secure networks, firewalls, safe handling of cardholder data, and regular security checks.
Many small businesses avoid storing raw card data by using hosted gateways or tokenization. This keeps them from handling sensitive data directly. Still, you must use a PCI-compliant provider. It’s not optional. It’s required to legally accept card payments online.
Authentication Mechanisms
Strong customer authentication ensures that the person paying is the actual card or wallet owner. This includes asking for CVV numbers, using 3-D Secure (with OTPs or passwords), and enabling features like biometrics or PINs for wallets and mobile payments.
For example, Indian rules from the RBI require extra authentication for most online card payments. That’s why Indian users get OTPs to finish their purchases. Two-factor steps like this help stop fraud.
Fraud Detection Tools
Most payment gateways and processors offer tools to detect fraud. These include AVS, which checks if the billing address matches the card, geolocation checks, and velocity checks that flag repeated fast transactions on the same card. They also use machine learning to find patterns that seem risky.
Merchants should use these tools with smart filters. You don’t want to block good users. But you must stop doubtful activity.
Tokenization & Secure Gateway Infrastructure
Always choose a trusted gateway or processor that prioritizes security. A reliable provider stores sensitive data safely and may use tokenization. Tokenization replaces real card numbers with random tokens. So even if your system is hacked, criminals get only useless tokens.
Protect Customer Data & Privacy
Security goes beyond payment info. Your whole site must be secure. Use encryption for saved passwords. Keep all software and plugins updated to avoid risks. Follow solid cybersecurity habits. Even leaks of non-financial data can break trust. Inside your business, limit who can access payment info. Only staff handling refunds or issues should view this data. Even then, hide the full card number.
Compliance with Local Regulations
In India, RBI rules cover tokenization and storage. Make sure your systems meet local legal needs. Since October 2022, the RBI mandates that merchants cannot store customers’ card numbers. Instead, tokenization must be used.
Conclusion
E-commerce payment systems are the lifeblood of online business. Without a reliable way to get paid online, even the best-looking site won’t succeed. For SMEs and business owners, especially in fast-growing markets like India, choosing the right payment systems can help your business grow faster. It lets you reach more customers.
In today’s world, business experience matters the most. A smooth, safe, and quick checkout is just as important as having a great product or nice-looking site. As one industry insight says, the payment system that gives the best user experience will lead in the future. This means your business should keep improving the way it handles payments. You can do this by adding popular payment options, making the process simpler, or improving security to meet what your customers expect.
This will create a shopping experience where customers feel safe and ready to click “Buy Now.” With the right system, you can focus on growing your business. Your customers, in turn, enjoy smooth and easy digital payments.