In the evolving financial landscape, access to the right type of credit can impact both personal stability and business growth. Whether you’re an individual managing everyday expenses or a business owner handling cash flow, understanding different credit structures, such as revolving credit, lines of credit, and installment loans, is essential for making the right decisions.
Credit is no longer limited to traditional bank loans. Modern borrowers rely on flexible tools like revolving lines of credit, Corporate credit cards, and business credit lines to manage working capital, fund purchases, or cover unexpected needs. These different credit options allow users to borrow, repay, and borrow again, giving them better control over their financial strategy.
What Is Revolving Credit?
Definition:
Revolving credit is defined as a type of credit facility where the borrower can repeatedly use funds up to a fixed limit, repay partially or fully, and continue using the available limit without submitting a new loan application. Interest is charged only on the amount utilized, not on the entire approved limit, making it cost-effective for short-term or unpredictable financial needs.
Revolving credit is a flexible borrowing option that allows individuals and businesses to access funds up to a pre-approved limit, use the credit as needed, repay the borrowed amount, and borrow again without reapplying. It is one of the most widely used credit types because it offers continuous access to money, making it ideal for managing short-term cash flow, emergencies, and recurring expenses.
Unlike long-term loans that provide a one-time lump sum, revolving credit works like a reusable pool of funds. As you repay your outstanding balance, your available credit limit is restored. This cycle of borrowing and repayment continues as long as the account remains active and payments are made on time.
Common examples of revolving credit include credit cards, personal lines of credit, and business lines of credit. For companies, a revolving business credit line becomes a powerful tool for managing operational costs, supplier payments, and seasonal demand.
Key Features of Revolving Credit
1. Flexible Borrowing
Borrowers can withdraw any amount within the approved limit whenever needed, making revolving credit highly adaptable for fluctuating expenses.
2. Reusable (Revolving) Credit Limit
As repayments are made, the credit becomes available again, allowing continuous borrowing without additional approvals.
3. Interest Only on the Used Amount
You only pay interest on the amount you actually use, which reduces unnecessary interest costs compared to traditional loans.
4. Variable Repayment Cycles
Revolving credit allows flexible repayment schedules. Borrowers can choose to pay the full balance, the minimum due, or any amount in between, depending on their financial situation.
What Is a Revolve Account?
A revolving account is a type of credit account usually connected to revolving credit, such as credit cards or lines of credit, where the borrower carries forward (or “revolves”) an unpaid balance from one billing cycle to the next. Instead of paying the full outstanding amount every month, the user can pay a minimum due and choose to carry forward the remaining balance. This remaining balance continues to accrue interest until it is fully repaid by the individual or business.
Revolve accounts are commonly used by individuals and businesses that need short-term liquidity or prefer flexible repayment schedules.
How Do Revolving Balances Work?
A revolving balance is the portion of your credit usage that you carry forward into the next billing period. Here’s how it works:
You spend using a revolving credit facility, such as a credit card or line of credit.
- At month-end, your statement shows the total outstanding amount.
- You can either pay the full amount or only the minimum due amount.
- Any unpaid amount becomes a revolving balance, which incurs interest daily until repaid.
- As you repay, your available credit limit gets restored, allowing you to borrow funds again.
This cycle gives borrowers flexibility but also increases the cost of borrowing if balances are not cleared regularly.
Impact of Revolving Behavior on Credit Score
Your credit utilization ratio, which is the percentage of credit you use compared to your total limit, is a major factor in your credit score. Revolving balances directly affect this ratio.
Revolving behavior affects your credit score in the following ways:
Positive Impact
- Paying on time consistently improves credit history.
- Maintaining a low revolving balance shows responsible credit management.
Negative Impact
- High revolving balances increase credit utilization, which can lower your credit score.
- Continuously revolving large amounts can signal risk to lenders.
- Missing payments or paying late leads to penalties and long-term credit score damage.
To maintain a healthy credit score, experts recommend keeping your utilization below 30% and avoiding long-term high revolving balances.
Revolving Credit and Line of Credit: What’s the difference?
Financial tools like credit cards, revolving credit facilities, and lines of credit help businesses manage cash flow and grow. Both revolving credit and lines of credit are designed to offer flexible funding based on borrowing requirements.
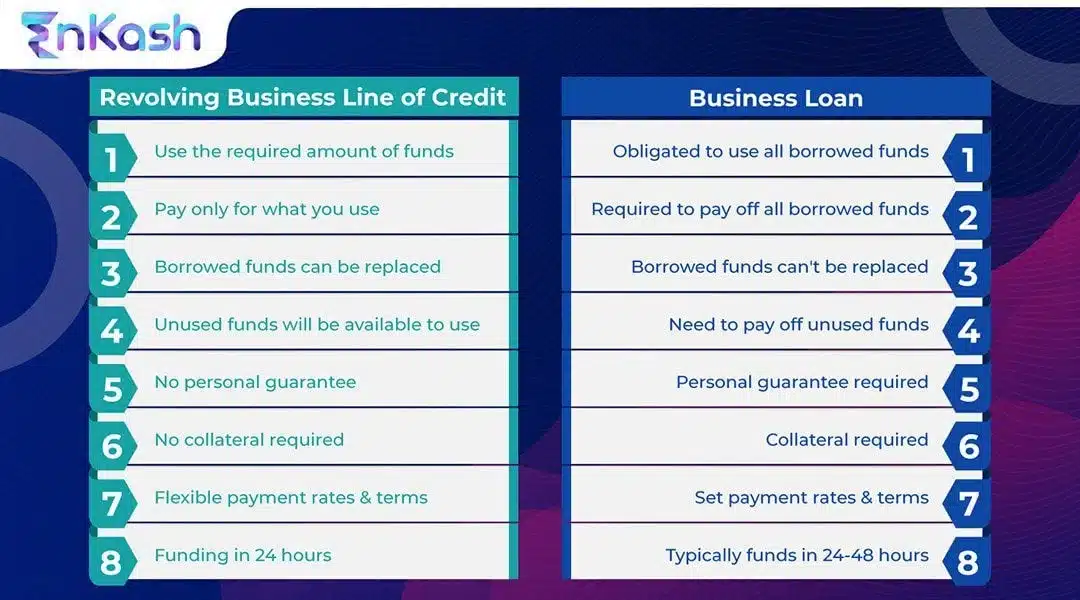
A revolving business line of credit allows a company to borrow, repay, and borrow again up to a fixed limit, until the lender or borrower closes the account. In contrast, a business term loan (non-revolving line of credit) is a one-time agreement. The full amount is disbursed once, repaid in instalments over a fixed tenure, and once repaid, the facility is closed and cannot be reused.
The criteria for issuing a line of credit depend on the business’s creditworthiness. The company can borrow up to the approved limit and repay partially or fully, as per the repayment terms. Based on the business’s repayment history and credit score, the lender or financial institution may decide to increase the credit limit, allowing the business to access more funds when required.
What is the Difference Between Installment Credit and Revolving Credit?
Feature |
Installment Credit |
Revolving Credit |
|---|---|---|
Definition |
A fixed loan repaid through scheduled EMIs over a specific tenure. |
A reusable credit limit where funds can be borrowed, repaid, and borrowed again. |
Borrowing Structure |
One-time lump-sum loan. |
Flexible borrowing as needed within the approved limit. |
Repayment |
Fixed monthly EMIs until the loan is fully repaid. |
Flexible repayment—pay full, partial, or minimum due. |
Interest Charges |
Usually lower, fixed interest rate. |
Higher interest, charged only on the used amount. |
Credit Limit |
Does not replenish after repayment. |
Limit resets as repayments are made. |
Best For |
Long-term goals like home loans, auto loans, and business expansion. |
Short-term cash flow needs, emergencies, and working capital. |
Examples |
Personal loan, car loan, home loan, business term loan. |
Credit cards, revolving line of credit, overdraft facilities. |
Impact on Credit Score |
Helps build credit with consistent EMI payments. |
Affects credit utilization; a high revolving balance may lower the score. |
Meaning and Significance of Line of Credit in India
A non-revolving line of credit is a one-time agreement between the borrower (business) and the lender. Once the borrowing party repays the entire amount, the non-revolving credit account is closed. Unlike a revolving facility, the borrower repays fixed instalments of principal and interest on preset due dates..
Example of Line of Credit India
For startup businesses in the growth stage, funds in the business account can be drained due to increased expenses. In that case, during payments, there is a high risk of cheques bouncing, which can affect the business’s creditworthiness in the long run. Businesses must manage their finances carefully to avoid such situations. Thus, to avoid check bouncing, the startups can apply for a line of credit to acquire overdraft protection when the balance is insufficient in the business account to make payments.
What are the Different Types of Credit?
Type of Credit |
Meaning |
Key Features |
Common Examples |
Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Revolving Credit |
A reusable credit limit where you can borrow, repay, and borrow again without reapplying. |
Flexible borrowing, interest only on the used amount, variable repayment. |
Credit cards, personal line of credit, business line of credit, overdraft. |
Short-term needs, working capital, emergencies, recurring expenses. |
Installment Credit |
A fixed loan repaid through equal monthly installments (EMIs) over a set tenure. |
Predictable EMIs, usually lower interest rates, structured payments. |
Personal loans, home loans, auto loans, consumer EMIs, business term loans. |
Long-term goals like buying a house, vehicle, or business expansion. |
Open Credit |
Credit that must be paid in full every billing cycle; balance cannot be carried forward. |
No revolving balance allowed, which promotes financial discipline. |
Utility bills, charge cards. |
Monthly expenses and payments that require full settlement each cycle. |
Can a business apply for instant loans without a credit score?
Revolving credit and line-of-credit facilities are designed to help businesses manage temporary financial shortfalls. Thus, many financial institutions offer the possibility of applying for a line of credit or instant loans without credit scores, but based on specific criteria that the lenders formulate to safeguard their interests.
Lenders may agree to offer a loan amount against the business’s assets, which are used as collateral. The lenders can also charge higher than standard interest rates on the loan amount sanctioned to the business.
Applying for a line of credit or instant loans without a credit score can be risky. However, many businesses still opt for it when analyzing the potential for their business growth. If a company has strong growth potential and a clear repayment plan, it may still be able to apply for instant loans without a traditional credit score.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between revolving credit, installment credit, and open credit is essential for making smarter financial decisions. Each credit type serves a unique purpose, whether it’s managing short-term expenses through a revolving line of credit, funding long-term goals with installment loans, or handling routine payments through open credit accounts. When used responsibly, these credit tools can strengthen your financial stability, improve cash flow, and support both personal and business growth.
As a borrower, it’s important to evaluate your financial needs, repayment capacity, and long-term goals before choosing a credit option. Keep your credit utilization low, maintain timely repayments, and monitor your credit score to ensure healthy financial behaviour. By understanding how each credit type works, you can confidently select the right borrowing solution and build a stronger financial foundation.
FAQs
1. What is a Line of Credit?
A line of credit (LOC) is a flexible borrowing facility that allows you to access funds up to a pre-approved limit whenever needed. You can borrow, repay, and borrow again as long as you stay within the limit. Interest is charged only on the amount you actually use, making it ideal for managing cash flow and short-term financial needs.
2. What Is an Example of a Line of Credit?
A common example of a line of credit is a credit card, where you receive a credit limit and can use it repeatedly by repaying the outstanding balance. Other examples include a personal line of credit, a home equity line of credit (HELOC), and a business line of credit used by companies to cover operational expenses or working capital needs.
3. What is a Revolving Line of Credit?
A revolving line of credit is a reusable credit facility where the credit limit resets as you repay the borrowed amount. This means you can withdraw funds, repay them, and access the limit again without reapplying. Credit cards, business credit lines, and overdraft accounts are the most common revolving credit options.
4. What is a Non-Revolving Line of Credit?
A non-revolving line of credit provides a fixed amount of funds that can be used once. After you use the approved amount and repay it, the credit line closes and cannot be used again. It works similarly to a one-time loan and is commonly used for specific purposes such as home renovation or education expenses.
5. How to Apply for a Revolving Line of Credit?
To apply for a revolving line of credit, follow these steps:
- Check eligibility with your bank, NBFC, or fintech lender.
- Submit KYC documents such as ID proof, address proof, and income statements.
- Provide financial details like bank statements, business revenue (for business LOCs), or salary slips (for personal LOCs).
- Choose your credit limit based on your repayment capacity.
- Complete verification and sign the agreement.
- Once approved, you get access to a flexible credit limit that can be used anytime.