A digital wallet is like a virtual pocket on your phone — it stores money, simplifies payments, and makes transactions fast and secure.
Among all wallet types, an open wallet stands out. It allows users to pay, receive, and — with full KYC — even withdraw cash or transfer funds across networks. These wallets operate under the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and follow the country’s Prepaid Payment Instrument (PPI) framework.
Open wallets offer the ideal mix of convenience and compliance, helping India’s digital payments ecosystem grow without compromising on security or trust.
What Is an Open Wallet
An open wallet gives users full control of their digital money. Unlike closed or semi-closed wallets tied to a single merchant or app, an open wallet can be used across banks, merchants, and platforms. You can pay bills, send funds, and even withdraw cash — all within the same regulated system.
Think of it as a unified rail that connects your funds with every place you want to spend. This flexibility and interoperability make open wallets a core pillar of India’s real-time payment ecosystem.
How It Differs from Other Digital Wallets
Every digital wallet looks similar at first glance, but they do not all work the same way. Some wallets, like closed types, let you spend only within a single app or brand. Semi-closed wallets take a small step ahead, allowing payments to a group of selected partners. An open wallet moves beyond those limits. It works across networks, supports cash withdrawals, and enables money transfers without boundaries.
Because the wallet connects directly with financial systems, it operates under strict regulatory supervision. The RBI Open wallet Guidelines make sure that such wallets meet all compliance checks, from full KYC verification to proper fund storage and transaction monitoring. These rules are what make open wallets reliable for both users and issuers.
Why Open Wallets Matter in Digital Payments
The open wallet concept goes beyond convenience — it drives inclusion and innovation in India’s cashless economy. A single wallet can handle multiple use cases: paying bills, sending money, or withdrawing cash — without switching apps.
For users, open wallets simplify financial access.
For businesses, they expand reach and enable faster settlements.
For the economy, they bring millions into the formal financial system by bridging cash and digital payments.
Open wallets help unify banks, fintechs, and consumers under a single interoperable framework, making digital transactions secure, transparent, and scalable.
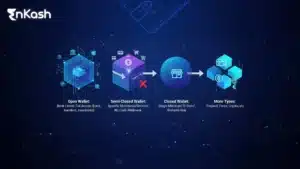
Types of Wallets and Where the Open Wallet Fits
Closed Wallets
A closed wallet is a basic form of a digital wallet that limits how money can be used. It is issued by a single company, and the stored value can be spent only within its own network. If you purchase something using this wallet, the refund goes back into it instead of your bank account. This model gives brands tighter control over payments but restricts users from using the balance elsewhere.
Semi-Closed Wallets
A semi-closed wallet extends a bit more flexibility. It works across a group of merchants who have a shared agreement with the wallet issuer. Users can pay bills, recharge, or shop with selected partners under the same network. Yet, this version still cannot handle cash withdrawals or open transfers. It is suited for users who want safe, small-scale digital transactions without linking their bank account directly.
Open Wallets
To understand the open wallet meaning, think of a tool that connects directly with regulated financial systems. It allows users to make payments, send money, and even withdraw cash across different banks and platforms. This freedom makes it a key part of the larger digital economy. Every example of an open wallet shows how interoperability builds trust and convenience together.
Such wallets are issued only by authorized PPI issuers licensed by the RBI. They must follow strict security and KYC standards to keep transactions transparent and compliant. These providers design systems that connect users, merchants, and banks within one seamless network.
Read More: What is UPI Wallet?
Real Examples and Applications of the Open Wallet
You’ll find open wallet functionality in apps that let users pay for groceries, send money to bank accounts, and withdraw cash from authorized outlets — all within one interface.
These wallets run on regulated payment rails, connecting directly with banks and merchant networks. Examples include bank-issued PPIs, co-branded prepaid cards, or wallets integrated with UPI and card networks.
- Users can pay anyone or transfer funds instantly.
- Merchants can accept payments from any compliant source.
- Businesses can settle funds faster and offer cash-out options to customers.
This balance of flexibility and security strengthens both consumer trust and merchant adoption.
White Label Open Wallets
Many brands use a white label open wallet or co-branded wallet model. In this setup, a licensed PPI issuer builds the infrastructure while another company offers it under its brand name.
For instance, a retailer or travel platform might launch its own wallet, but the backend is managed by a regulated provider.
This approach helps businesses:
- Launch faster without seeking individual RBI approval
- Ensure compliance and KYC coverage
- Retain customer ownership and brand identity
White-label wallets are increasingly popular across e-commerce, fintech, and loyalty platforms because they combine brand control with regulatory safety.
Open Wallet Software and Integration
The true power of an open wallet lies in its software infrastructure.
An open wallet software system includes tools for:
- KYC verification and onboarding
- Merchant integration via APIs
- Real-time reconciliation and reporting
- Escrow fund management
With seamless open wallet integration, businesses can handle payments, refunds, and balances without rebuilding their core systems.
For developers, it offers scalability; for merchants, reliability; for users, simplicity.
API-driven integration also supports loyalty, EMI, and subscription services — all within RBI’s secure financial network.
Impact on India’s Digital Finance Landscape
The rise of open wallets has redefined digital payments in India. They enable financial inclusion, reduce reliance on cash, and promote regulated innovation in fintech.
Each open wallet example demonstrates how interoperability empowers both consumers and businesses. As more RBI-authorized wallet service providers adopt advanced integration standards, India’s digital economy moves closer to a connected, cash-light future.
Business Value and Use Cases of Open Wallets
For Merchants and Businesses
An open wallet lets merchants accept payments from a wide network of users without relying on a single payment gateway.
Benefits include:
- Faster settlements
- Lower cash handling costs
- Access to multi-channel customers
Since open wallets operate under RBI-regulated payment structures, every transaction is traceable and secure. Businesses can also integrate loyalty or rewards programs within their wallet ecosystem, encouraging repeat use.
For Financial Institutions and Fintech Companies
Banks and fintech firms leverage open wallets to expand digital offerings.
By partnering with licensed PPI providers, they can launch wallet products quickly using pre-certified technology frameworks that comply with all RBI guidelines.
This collaboration lets:
- Banks focus on customer engagement
- Service providers handle compliance, security, and tech operations
- Users enjoy a consistent payment experience across apps
Such partnerships accelerate financial inclusion while reducing development and maintenance costs.
For Platform Operators and Ecosystem Builders
Large digital platforms now embed white-label open wallets to manage payments internally.
This strategy:
- Keeps user data and branding in-house
- Reduces dependency on third-party gateways
- Enables new services like credit lines, rewards, and cross-platform payments
In short, open wallets convert regular user engagement into measurable revenue and retention.
Regulatory and Compliance Framework for the Open Wallet
Governance Under the PPI Framework
An open wallet is categorized under Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) as per RBI’s Master Directions. Only authorized banks and non-bank entities can issue such wallets after obtaining a license.
These issuers must:
- Maintain escrow accounts with scheduled commercial banks
- Conduct periodic reporting and audits
- Implement KYC and data protection protocols
The goal is to make every digital transaction secure, traceable, and compliant.
Core RBI Open wallet Guidelines
The RBI guidelines define the operating boundaries for open wallets:
- Full KYC is mandatory for activation and usage
- Wallet balances must be ring-fenced in escrow accounts
- Transactions are permitted for merchant payments, fund transfers, and cash withdrawals
- Issuers must maintain audit trails and reconciliation logs
These checks ensure that funds remain protected even if a wallet provider faces operational issues.
Rules for Interoperability and Security
One of the key principles in the RBI Open Wallet Guidelines is interoperability. As per RBI’s interoperability mandate, every open and full-KYC semi-closed wallet must interoperate with UPI and other payment systems. This means users can pay or transfer money freely between accounts without barriers. It helps build a unified network where every user has equal access to digital payments.
Security plays an equally strong role. Wallet issuers must adopt multi-factor authentication, encryption, and fraud detection tools that work in real time. Alerts are mandatory for all debit or credit transactions. These checks keep users informed and help prevent unauthorized use.
Risk Control and Customer Protection
The regulatory body also places a strong focus on grievance redressal. Issuers must provide a defined grievance redressal mechanism, often through 24×7 channels or within RBI-specified timelines. Periodic system audits, data privacy measures, and operational resilience checks are also part of the standard process.
By enforcing these measures, the regulator ensures that digital payment systems remain safe and transparent. The open wallet operates with the freedom to serve large audiences but within a framework that values security and accountability. This balance allows innovation to grow without risking user trust.
Technical and Implementation Aspects of the Open Wallet
Core Architecture and Functionality
An open wallet relies on a strong technical framework that connects users, merchants, and banks within one ecosystem. The wallet’s structure includes modules for fund management, merchant onboarding, real-time transaction monitoring, and escrow settlement. Each layer works in sync to ensure the money moves safely from one point to another.
The core engine processes thousands of transactions per second while maintaining accuracy. It verifies user details through KYC, encrypts sensitive data, and reconciles payments instantly. A secure open wallet software platform must handle all of this seamlessly without lag or downtime.
Integration with Merchants and Partners
Smooth open wallet integration is what makes the entire system efficient. Merchants use APIs that connect their websites, point-of-sale systems, or apps with the wallet’s infrastructure. Once integrated, payments, refunds, and settlements happen automatically. This reduces errors, saves time, and gives businesses a cleaner, faster checkout flow.
Integration also extends to loyalty systems, EMI services, and third-party payment gateways. Every partner must meet the same security and compliance checks before going live. That uniformity is what builds long-term trust in digital payments.
Security Layers and Fraud Prevention
Every wallet transaction runs through strict checks for risk and authentication. Multi-factor verification, biometric login, and behavioral analytics help detect irregular activities before they cause damage. Real-time alerts keep users informed of every debit or credit action, preventing misuse.
The open wallet service providers implement risk-scoring systems that flag unusual patterns such as repeated failed logins or unexpected transaction sizes. These alerts allow quick investigation and prevent larger financial threats.
White Label Models and Scalability
A white label open wallet solution lets companies offer a wallet under their own brand without building the full system themselves. The provider handles the backend, compliance, and maintenance while the business focuses on user experience. This partnership speeds up deployment and helps brands maintain consistent quality across devices and markets.
Scalability remains a key requirement. As transaction volumes grow, the wallet’s infrastructure must expand without slowing performance. Cloud-based systems make this easier, letting open wallet service providers upgrade capacity as user demand increases.
Selecting the Best Open Source Wallet Framework
While open-source frameworks can help prototype or test features, production-grade regulated wallets must operate under an authorized PPI license. Open source tools offer flexibility and transparency, allowing teams to modify features based on local compliance and security needs.
However, choosing the right one depends on community support, regular code audits, and modularity. Any open source system used for regulated payments must still meet the same KYC, escrow, and encryption standards as commercial platforms. A strong foundation keeps both businesses and users safe while encouraging innovation within the digital wallet landscape.
In Conclusion
An open wallet represents freedom within a regulated structure. It connects users, merchants, and banks through secure, interoperable systems that keep transactions transparent and fast. By following the RBI Open wallet Guidelines, issuers create trust and safety while expanding digital access for everyone. Businesses gain reach, users gain control, and regulators ensure accountability. As technology and compliance continue to evolve, the digital wallet ecosystem will keep growing stronger. The open wallet sits at the center, linking payment systems and shaping the next phase of digital payments built on trust, accessibility, and real innovation.
FAQs
1. What is the key purpose of an open wallet in digital payments?
To enable users to pay, transfer, and withdraw funds across banks and platforms under a regulated system. It connects directly with RBI-authorized networks for seamless, secure transactions.
2. Can an open wallet be used for international transactions?
Mostly, open wallets cater to domestic transactions. Cross-border use depends on partnerships with licensed entities and adherence to foreign exchange and AML guidelines.
3. Is full KYC mandatory for open wallets?
Yes. Users must complete full KYC verification before accessing all features. This ensures transparency and prevents misuse.
4. What happens if an open wallet provider loses its authorization?
If a provider loses authorization, the open wallet service providers must stop onboarding new users and notify existing ones. Funds already stored in escrow accounts remain protected under banking supervision. Users can withdraw or transfer their balance to another compliant wallet or bank account as per regulatory instructions.
5. Is it safe to link multiple bank accounts with an open wallet?
Yes, it is safe when managed through verified networks. Linking multiple bank accounts to an open wallet allows users to switch payment sources easily. The data travels through encrypted channels, and all transactions follow multi-layer authentication. This setup helps users enjoy convenience without compromising on safety or privacy.
6. How are disputes and failed transactions resolved in open wallets?
Every open wallet provider must have a clear customer redressal system in place. Users can report failed or delayed payments through app support or customer care channels. The provider investigates and reverses valid cases within specific timelines. Regular audits and central oversight make sure that user complaints are resolved fairly and efficiently.
7. Can businesses build custom wallets using open wallet software?
Yes, companies can use licensed open wallet software or white-label frameworks to build their own branded wallets. These setups include all compliance, escrow, and verification systems required by regulators. Businesses can personalize user interfaces and add loyalty features while keeping the operational side managed by certified technology providers.
8. What kind of users benefit most from open wallets?
Open wallets help both consumers and businesses. Regular users gain flexibility to pay or withdraw across networks, while merchants receive payments from any compliant source. It suits people who rely on frequent digital transactions and organizations looking to expand their reach without managing complex payment infrastructure.
9. How do open wallets contribute to financial inclusion?
An open wallet allows anyone with verified credentials to access digital payments, even without a traditional bank account. It reduces cash dependency and simplifies money transfers in smaller markets. By giving users an affordable and secure tool, open wallets support broader participation in formal financial systems.
10. What future innovations are expected in the open wallet ecosystem?
The next phase for digital wallet systems will include stronger integration with biometric identity, AI-driven fraud detection, and real-time data analytics. Service providers may add micro-credit or insurance features under strict oversight. These developments will enhance user experience while ensuring that open wallets remain secure and compliant across all channels.